Lean Six Sigma Combined with Blockchain for Improved Efficiency

In the continuously changing and progressing world of business and industries, Lean Six Sigma has become the gold standard for successfully assessing and fixing processes via project management. Lean Six Sigma is considered a best practice because it uses established and proven tools integral to its efficient methodologies.
Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-driven concept focusing on defect prevention over defect detection. It drives customer satisfaction and bottom-line results by reducing variation, waste, and cycle time while promoting work standardization and flow, thereby creating a competitive advantage.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma, sometimes called Lean Sigma, is a management approach that blends two powerful strategies: Lean and Six Sigma.
What is Lean in Lean Six Sigma?
Lean focuses on streamlining processes. The main idea here is to eliminate waste – anything that doesn’t add value to the customer. This could be anything from unnecessary steps in a process to excessive inventory. By eliminating these, businesses can become more efficient, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
What is “Six Sigma” in Lean Sigma?
Six Sigma, on the other hand, is all about improving quality. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s, it uses tools and techniques to identify and reduce process errors and variability. The goal is to make processes more predictable and consistent, leading to higher-quality products and services.
When combined, Lean Sigma offers a comprehensive approach to improving business performance. It helps companies do things better (thanks to Six Sigma) and faster (thanks to Lean) while reducing costs.
DMAIC Process in Lean Six Sigma
The Lean Sigma methodology often follows a structured process, typically referred to as DMAIC:
- Define: Identify the problem or opportunity for improvement.
- Measure: Collect data to understand the current process and establish a baseline.
- Analyze: Examine the data to find the root causes of issues.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address these root causes.
- Control: Establish systems to ensure that the improvements are sustainable.
Lean Six Sigma can be applied in various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and government, to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality.
It’s a versatile, data-driven approach that empowers teams to make informed decisions and drive meaningful change in their organizations.
Lean Six Sigma Explanation Diagram
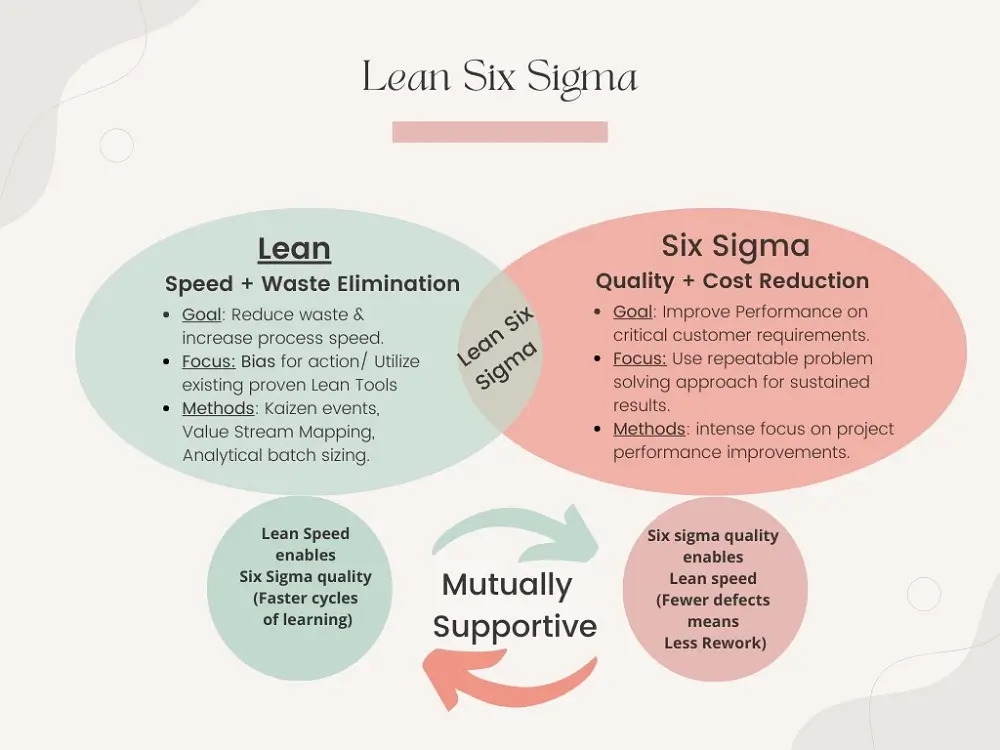
Lean Six Sigma is a discipline of project management that helps organizations deliver optimal customer value via efficient operations and consistent quality standards.
This methodology systematically improves performance by strategically reducing wastage and removing undesirable variations.
So, Lean Six Sigma encompasses a variety of tools that enable organizations to improve overall customer satisfaction, maintain their quality, offer high-grade products and services, and improve their bottom line. This discipline results in the creation of excellent problem-solving skills that have the power to transform any organization.
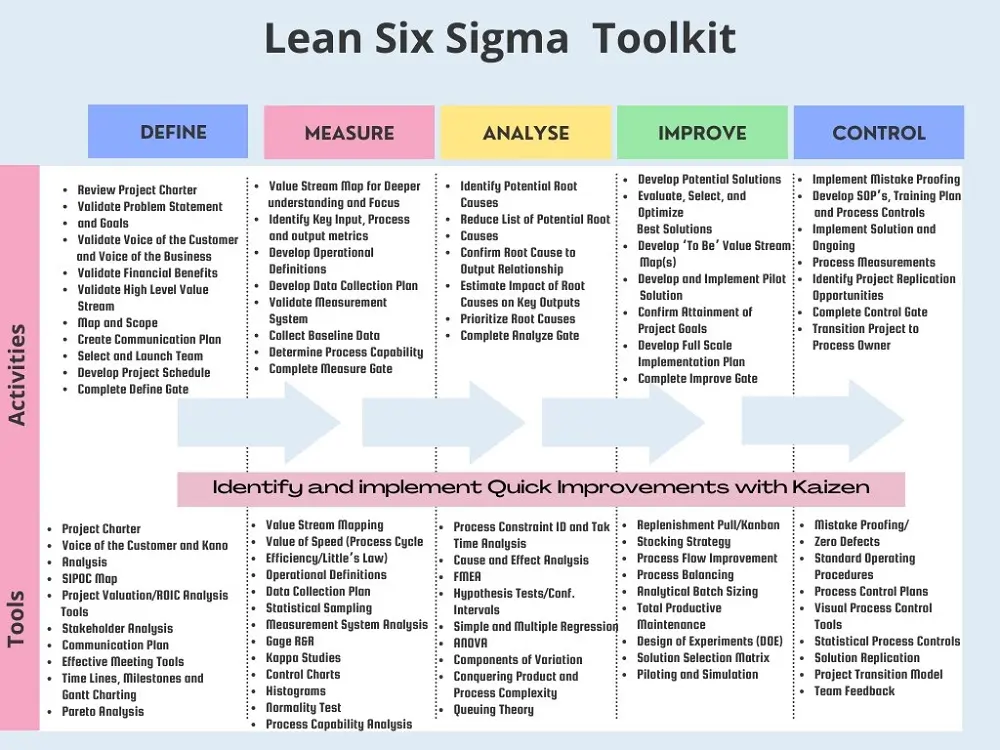
The table below summarizes the Lean Six Sigma toolkit that enables organizations to improve overall customer satisfaction, maintain quality, offer high-grade products and services, and improve their bottom line.
Lean Six Sigma Toolkit
Lean Six Sigma’s Application in Information Technology
When applied to information technology (IT), Lean Six Sigma becomes a powerful tool for enhancing efficiency and quality in IT processes and services. In the IT sector, Lean Six Sigma focuses on streamlining workflows, reducing waste, and improving service quality while emphasizing customer value.
Key Aspects of Lean Six Sigma in IT:
- Eliminating Waste: In IT, waste can manifest as redundant processes, excessive documentation, underused resources, or over-engineering. Lean Sigma helps identify and eliminate these inefficiencies, leading to faster and more cost-effective service delivery.
- Improving Processes: IT processes, whether related to software development, network management, or customer support, often have room for improvement. Lean Sigma tools like flowcharts, root cause analysis, and Pareto charts help understand and refine these processes.
- Enhancing Quality: Six Sigma’s emphasis on reducing variability and defects is particularly relevant in IT. By applying Six Sigma methodologies, IT teams can reduce bugs in software, minimize downtime in systems, and enhance the overall quality of IT services.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Lean Six Sigma in IT relies heavily on data and metrics. Whether it’s measuring system uptime, response times, or bug rates, Lean Sigma uses quantitative data to make informed decisions, leading to more effective problem-solving and process optimization.
- Customer Focus: At its core, Lean Six Sigma aims to increase value for the customer. In IT, this means ensuring that services are reliable, responsive, and aligned with user needs and expectations.
- DMAIC in IT: The DMAIC framework is equally applicable in IT. For example, in a software development process: “Define” could involve outlining a new feature based on customer feedback. “Measure” might involve tracking development progress or bug counts. “Analyze” could identify bottlenecks in the development process. “Improve” could involve streamlining the development workflow. “Control” could mean implementing ongoing monitoring of the new feature’s performance.
Applications in IT:
- Software Development: Streamlining development processes, reducing bugs, and enhancing software quality.
- IT Service Management: Improving helpdesk operations, reducing ticket resolution times, and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Network Management: Enhancing uptime, optimizing network performance, and ensuring security.
Lean Six Sigma in IT is not a one-time project but a continuous journey toward process improvement and customer satisfaction. By integrating Lean Sigma principles into their operations, IT departments can significantly enhance their efficiency, service quality, and ability to adapt to changing technological landscapes.
Blockchain and Lean Six Sigma
Before we get into the application of Lean Sigma for blockchain, let’s have a quick recap.
Blockchain
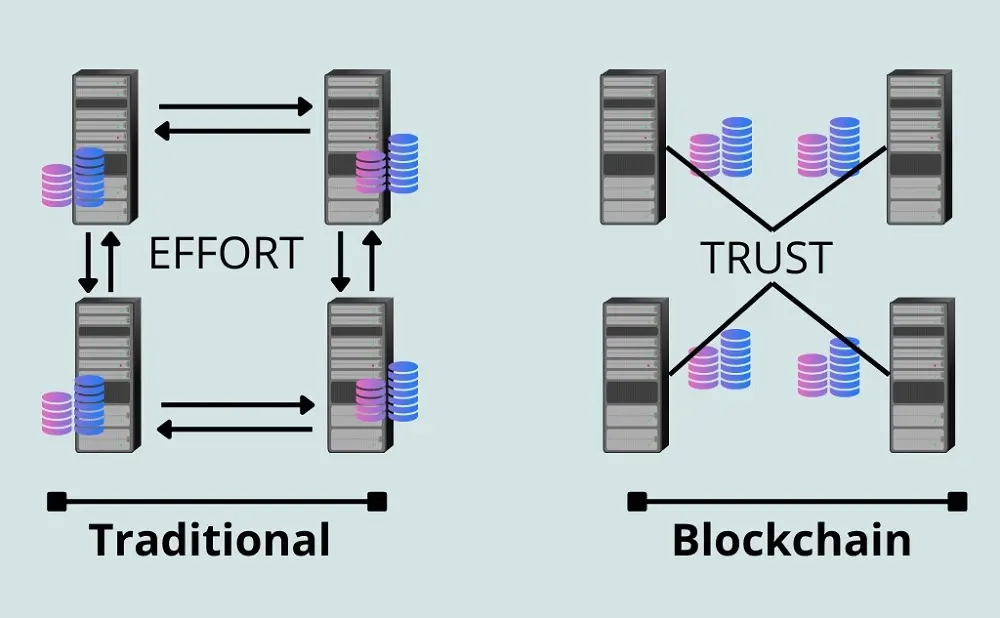
A blockchain is designed to create a fully secure source of transaction history that cannot be tweaked or edited in any way. Blockchain is a big idea that is slowly revolutionizing the world. It is also how bitcoins and other digitized cryptocurrencies are powered.
Blockchain functions solely based on trust or its lack thereof, depending on your paradigm. Adopting a blockchain approach to data management, verification, and storage reduces the need for intermediaries and eliminates the friction that gets in the way.
Blockchain is a new way of storing data in a distributed ledger, allowing multiple stakeholders to confidently and securely share access to the same information. Only stakeholders that need to see the data will have access. In addition, all stakeholders will know if anyone tries to tamper with, duplicate, or alter any part of the data.
Blockchain technology provides the new infrastructure to build the next generation of applications. Imagine ecosystem partners having access to the same data in near real-time—not a copy of the data, but the actual data itself, including its activity history. A single source of truth in the data means validation no longer relies on a primitive system of back-and-forth checks and reconciliation. Instead, it could be as simple as “I see what you see.”
But blockchain is only the start. As the technology has matured, so will the capabilities to support these growing ecosystems. We call this combination of technologies Multiparty Systems.
Multiparty Systems include blockchain, distributed ledger, distributed database, tokenization, and various other capabilities. Such a system enables a shared data infrastructure between individuals and organizations that drive efficiency and build new business and revenue models.
How does a blockchain fit into a Lean Six Sigma approach to project management?
The answer lies in the different qualities and standards that both Lean Six Sigma and blockchain rely on.
From a blockchain perspective, it offers several qualities that perfectly complement the Lean Six Sigma operating model. DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control) is the most common methodology within a Lean Six Sigma approach.
The four key characteristics of a blockchain that make it an incredible piece of technology are consensus, provenance, data immutability, and finality.
Characteristics of Blockchain Complementing Lean Six Sigma
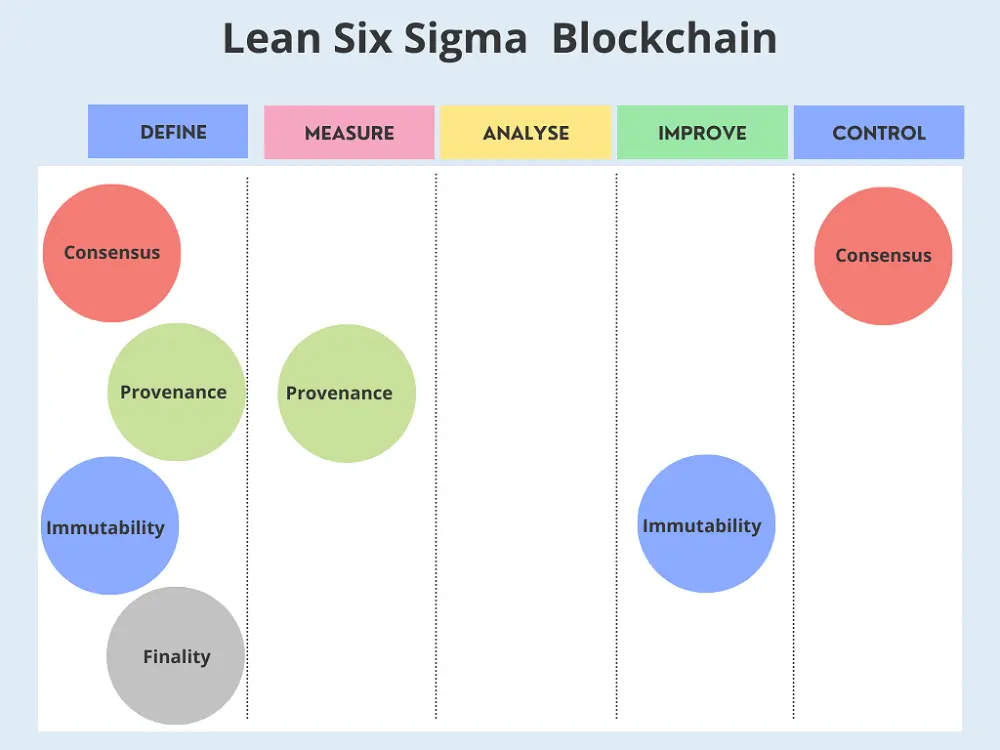
Understanding their comparative and complementary characteristics crucial to explore how blockchain and Lean Six Sigma methodology go hand in hand.
All the attributes of a blockchain will come in handy during the first phase of Lean Six Sigma to define a process or a problem. This is because the structure of the blockchain infrastructure is such that it’s based on clear tracking of data, data traceability, and ownership.
All the above aspects are backed by records of all those involved in it, regardless of where they are situated. This is important because we can not define effectively without the needed source data to analyze what it is about. If we can not define the problem, it is highly unlikely that we can address and solve it.
Provenance
Provenance is the next aspect of the blockchain that ties in nicely with the Lean Six Sigma methodology. This goes hand in hand with its ability to measure a process by demonstrating the specific root of an asset and how it has changed over time. This data, in turn, comes in handy for assessing the overall efficiency of a specific process. A similar concept is also prevalent in Lean Six Sigma, where the efficiency of a process is improved based on how it is done.
Lean Six Sigma is closely associated with control standards for improved efficiency. This is where the consensus element of the blockchain steps into play.
Lean Six Sigma and Consensus in Blockchain
Consensus helps validate the transactions before they can be recorded on the blockchain. The immutability characteristic of a blockchain can also be leveraged to assist with improvement. This is because the immutability of the blockchain is the point at which:
- Transaction history shows all the past transactions
- It also shows the improvements made and implemented.
This helps obtain the data needed to determine the failure rate and the inputs needed to determine the costs associated with poor quality.
Usually, most decisions in organizations and businesses alike are made based on thinking and brainstorming within departments or company silos.
Unfortunately, such working, coordination, and decision-making methods can lull departments and even organizations to believe they have completely gone Lean, only to realize that the entire chain of processes is less than sub-optimal.
Optimization
The next important point in a blockchain is the optimization. Where Lean Six Sigma focuses on systems and processes prevalent in the organization, blockchain forces them to think of more efficient forms of cooperation previously unthought of, such as system integration with suppliers or competitors.
How Blockchain Enhances Lean Six Sigma in Project Management:
- Data Integrity and Traceability: Blockchain provides a secure and immutable ledger, which ensures that all project data (like performance metrics, process changes, and project updates) is accurate and unalterable. This feature supports the Six Sigma emphasis on data-driven decision-making.
- Transparency and Accountability: In a Lean Six Sigma project, transparency is key to process improvement. Blockchain’s transparent ledger allows all stakeholders to see the history of changes, decisions, and transactions, thereby fostering a culture of accountability and open communication.
- Streamlined Processes: Blockchain can automate many routine tasks through smart contracts — self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. This automation aligns with Lean principles by reducing waste and increasing efficiency, especially in administrative aspects of project management.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Blockchain platforms can facilitate better collaboration between teams and departments. Since blockchain operates on a decentralized network, it allows multiple parties to interact and collaborate without needing a central authority, which can speed up processes and decision-making.
- Quality Control: Blockchain technology can record and track quality metrics throughout a project’s lifecycle. This consistent and unchangeable record-keeping aids in Six Sigma’s quality improvement and defect reduction goal.
- Risk Management: Using blockchain in project management helps identify and document risks in a tamper-proof manner. This aids in the Lean Six Sigma process of risk assessment and mitigation, ensuring that projects are efficient and secure.
- Customer Focus: Lean Six Sigma emphasizes value creation for the customer. Blockchain can enhance this by providing a transparent view of the project process and progress, leading to increased customer trust and satisfaction.
Application Examples:
- Supply Chain Management Projects: Blockchain can track materials and products throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and efficiency, which is crucial for Lean Six Sigma initiatives.
- IT and Software Development Projects: Managing code changes, development stages, and bug tracking through a blockchain can enhance accountability and streamline development.
- Construction Projects: Tracking materials, work progress, and contractor performance on a blockchain can help in maintaining schedules and reducing waste, aligning with Lean principles.
Conclusion
As you can see, the blockchain infrastructure is the perfect setup for lean Six Sigma projects.
The qualities that define the blockchain also enable Lean Six Sigma in ways a conventional database fails. Lean Six Sigma focuses on improving efficiency, reducing wastage, and enhancing overall productivity and quality.
When blockchain technology is added, its value is enhanced to another dimension. Since the blockchain’s technical features can be perfectly aligned with any means of improving a business’s operations, profitability, and productivity, it can be easily paired with process methodologies such as Lean Six Sigma. When combined, they become a valuable and profitable business value proposition.
Integrating blockchain into Lean Six Sigma for project management represents a forward-thinking approach that leverages technology to enhance process efficiency, data reliability, and stakeholder trust. It’s a synergy that can bring significant improvements in the way projects are managed and executed

Nisha Arya is a Data Scientist and Technical writer from London.
Having worked in the world of Data Science, she is particularly interested in providing Data Science career advice or tutorials and theory-based knowledge around Data Science. She is a keen learner seeking to broaden her tech knowledge and writing skills while helping guide others.
